Inflammation is a normal immune response to injury or infection. It helps the body repair damaged tissue and fight off foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses.
However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to a wide range of health problems and diseases, such as fatigue, poor sleep, respiratory problems, digestive issues, and change in mood.
In this article we will explore the at risk groups, key signs of inflamation, and proven ways to reduce unwanted bodily inflammation.
Contents
About Chronic Inflammation
When the body senses an injury or infection, it activates immune cells and releases chemicals and signaling molecules to help repair damaged tissue and fight off foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. These chemicals and signaling molecules, called cytokines, help coordinate the immune response and attract immune cells to the site of injury or infection.
Inflammation can also be triggered by other factors, such as exposure to environmental toxins, chronic stress, and certain medical conditions. In these cases, the immune system may mistakenly attack healthy cells and tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
Inflammation is a complex process that involves multiple steps and involves the activation of immune cells and the release of cytokines, which are proteins that help coordinate the immune response. Excess cytokines can contribute to inflammation.
Inflammation is an important part of the immune system, but when it becomes chronic, it can contribute to the development of a range of health problems.
People Most at Risk of Chronic Inflamation
Chronic inflammation can affect people of all ages and genders, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing chronic inflammation.
These include:
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of chronic inflammation because excess fat tissue releases substances that can contribute to inflammation. Inflammation can then contribute to the development of a range of health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer (1).
- Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of chronic inflammation (2).
- Lack of physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of chronic inflammation (3).
- Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation (4).
- Smoking: Smoking is a major contributor to inflammation and can increase the risk of numerous health problems (5).
- Exposure to environmental toxins: Certain chemicals, such as those found in some household cleaners and personal care products, can increase inflammation (6).
- Age: As people age, they may be more likely to develop chronic inflammation (7).
10 Signs You're Suffering from Chronic Inflamation
Here are 10 signs that you may be experiencing chronic inflammation, and some evidence-based advice to help you reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
1. Persistent Pain or Discomfort
One of the most common signs of chronic inflammation is persistent pain or discomfort. This can occur in many forms, including muscle aches, joint pain, abdominal pain, and headaches.
If you have ongoing pain or discomfort that doesn't seem to have an obvious cause such as injury from exercise, it could be a sign of chronic inflammation.
2. Swelling or Redness
Inflammation is often accompanied by swelling and redness in the affected area.
If you have unexplained swelling or redness that does not go away, it could be a sign of chronic inflammation, especially if it is in more than one area of your body.
3. Fatigue
Chronic inflammation can also cause fatigue. You may experience low energy and consistent tiredness. If you are consistently feeling tired and unable to get through the day, you may be experiencing symptoms of inflammation.
4. Weight Gain or Loss
Inflammation can affect the body's metabolism and cause weight gain or weight loss. If you are putting on weight or losing weight, and it can't be explained by excess calorie intake, you may be experiencing the effects of chronic inflammation.
5. Difficulty Sleeping
Chronic inflammation can disrupt the body's natural sleep patterns, leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. If you usually sleep well but have begun experiencing disrupted sleep , this could be a sign of chronic inflammation.
6. Mood Changes
Inflammation can also affect the brain and contribute to mood change. You may experience increased irritability, anxiety, or even depression. If you are experiencing significant changes in your mood, you should consult a physician.
7. Skin Changes
Inflammation can cause changes in the skin, such as rashes, acne, or eczema. If you are experiencing unexplained changes in your skin, it could be a sign of chronic inflammation.
8. Digestive issues
Chronic inflammation can also cause digestive issues, such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or constipation. If you are experiencing ongoing digestive issues, consult your doctor immediately.
9. Respiratory Problems
Inflammation can also affect the respiratory system and cause issues such as persistent coughing, shortness of breath, or congestion. If you are experiencing respiratory problems that do not have an obvious cause, you should seek medical help.
10. Autoimmune Disorders
Chronic inflammation can also contribute to the development of autoimmune disorders, in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues. If you have been diagnosed with an autoimmune disorder, chronic inflammation is probably a contributing factor.
9 Proven Ways to Reduce Inflammation
If you are experiencing any of the above signs, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional. Chronic inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, including diet, stress, and underlying health conditions. A healthcare professional can help identify the cause of your chronic inflammation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
That being said, you can take action today to reduce inflammation in your body.
There are several natural ways to reduce chronic inflammation:
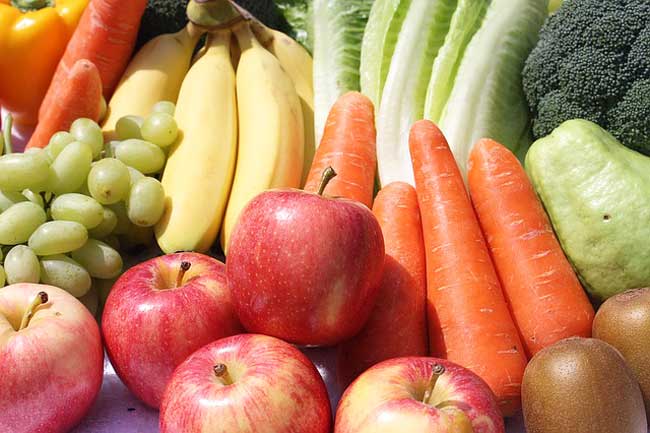
1. Eat a Whole-Foods-Plant-Based Diet
Some research suggests that a plant-based diet may be associated with a reduced risk of chronic inflammation.
* Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are rich in antioxidants and other substances that may have anti-inflammatory properties. Legumes, such as beans and lentils, are high in fiber and contain compounds that may also have anti-inflammatory effects. A plant-based diet may also be low in saturated fat, which has been linked to inflammation in some studies (8, 9, 10, 11).
However, it is important to note that the relationship between diet and inflammation is complex, and the potential effects of a plant-based diet on inflammation depend on a variety of factors, including overall diet, lifestyle, and genetics.
*Read about specific foods that reduce inflammation here.
2. Lower Processed Foods & Meat Consumption
Numerous studies have suggested that a diet high in red and processed meats may be associated with an increased risk of chronic inflammation. Red meat is high in saturated fat, which has been linked to inflammation. Processed meats, such as bacon, sausage, and deli meats, often contain preservatives and other additives that may contribute to inflammation.
In addition, processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated and trans fats can increase inflammation (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17).
3. Take Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking, running, or cycling, on most days of the week (18).
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can increase inflammation, so it is important to find ways to manage stress effectively. This may include practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, getting enough sleep, and finding healthy ways to cope with stress.
5. Reduce Alcohol Intake
Alcohol consumption can increase inflammation in a number of ways. No alcohol is best, but at the very least avoid heavy drinking.
Heavy alcohol consumption, defined as more than two drinks per day for men and more than one drink per day for women, is associated with an increased risk of chronic inflammation and numerous health problems (19).
6. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major contributor to inflammation and can increase the risk of numerous health problems. Quitting smoking can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health (21).
7. Get Enough Sleep
Lack of sleep can increase inflammation, so it is important to get enough rest. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night (22).
8. Avoid Environmental Toxins
Certain chemicals, such as those found in some household cleaners and personal care products, can increase inflammation. Choosing natural, non-toxic alternatives can help reduce inflammation.
9. Take Dietary Supplements
Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin may have anti-inflammatory properties. If you take prescription medication, speak to your healthcare professional before taking supplements, as they can interact with medication and have potential side effects (23, 24).
In Summary
While chronic inflammation is a serious health risk, the good news is that there are several natural ways to reduce it and improve your health.
These include eating a plant-based-whole-foods diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, quitting smoking, getting enough sleep, and avoiding environmental toxins as much as you can.
At the very least, maintaining a healthy weight, taking daily exercise, and eating more fruits, vegetables and whole grains will definitely reduce inflammation and improve your overall health.




(i) Stop drinking hot drinks – if the body is inflammed hot drinks make it even worse and (ii) take stinging nettle tincture and rub inflammed joints with the leaves.
Jan 31, 2023 at 12:58 pm
Thanks Elisabeth. I’d not heard that hot drinks make inflamation worse. Is there any information you can link me to? I do like a nettle tea too, but I guess I won’t have it too hot!
Jan 31, 2023 at 1:07 pm